Your Mental Health and Food

Did you know there is mounting evidence that is showing the food we eat can influence mental health and well being? In addition, our mental health and stress level also influences what we choose to eat. The gut-brain connection is showing that mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression are impacted by the food we eat and our gut microbiome. Multiple Long-term cohort studies suggest that those who follow a healthy diet, which is defined as including fruits, vegetables, whole grains and fish, are at a reduced risk for depression.
Gut Brain Health and Neurotransmitters
Research into the gut-brain connection in relation to mood is looking at the production of neurochemicals in the gut. Specifically serotonin and dopamine are major neurotransmitters that impact mood, sleep and motivation. Approximately 70% of these neurotransmitters are made in the gut. Crucial nutrients for brain health as well as gut health include fatty acids, protein, fiber, and B and D vitamins. The amino acids from protein rich foods are the starting point for neurotransmitter production and points to the importance of protein in the diet.
While there are many factors related to mental health including genetic and environmental, increasing evidence indicates a strong association between a poor diet and the exacerbation of mood disorders, including anxiety and depression, as well as other neuropsychiatric conditions.
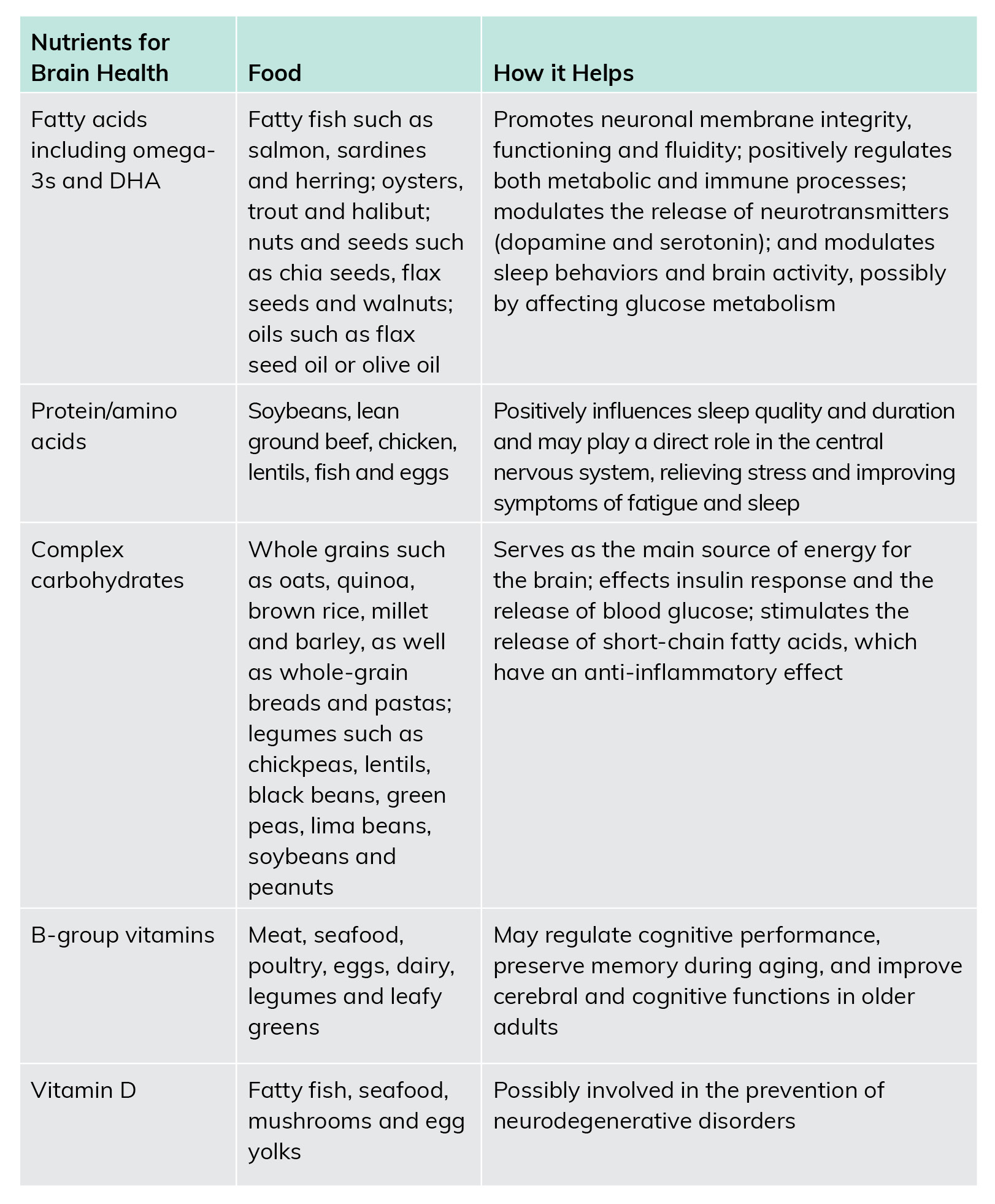
Nutrients for Mental Well Being
The chart below shows nutrients and corresponding foods that have been shown to be beneficial for brain health and mental well-being.
Crossroads To Health located in Acton, Ma works with a variety of conditions including mental health. If you'd like more information on how you can benefit schedule a complimentary discovery call here.

